-
Research Article
-
Increased but Not Increased: A Policy Impact Analysis of the Indoor Temperature Compliance Regulation
늘었지만 늘지 않았다: 적정실내온도 준수 규정의 정책 효과 분석
-
Jinmahn Jo, Jongwoo Kim, Sangkyu Park
조진만, 김종우, 박상규
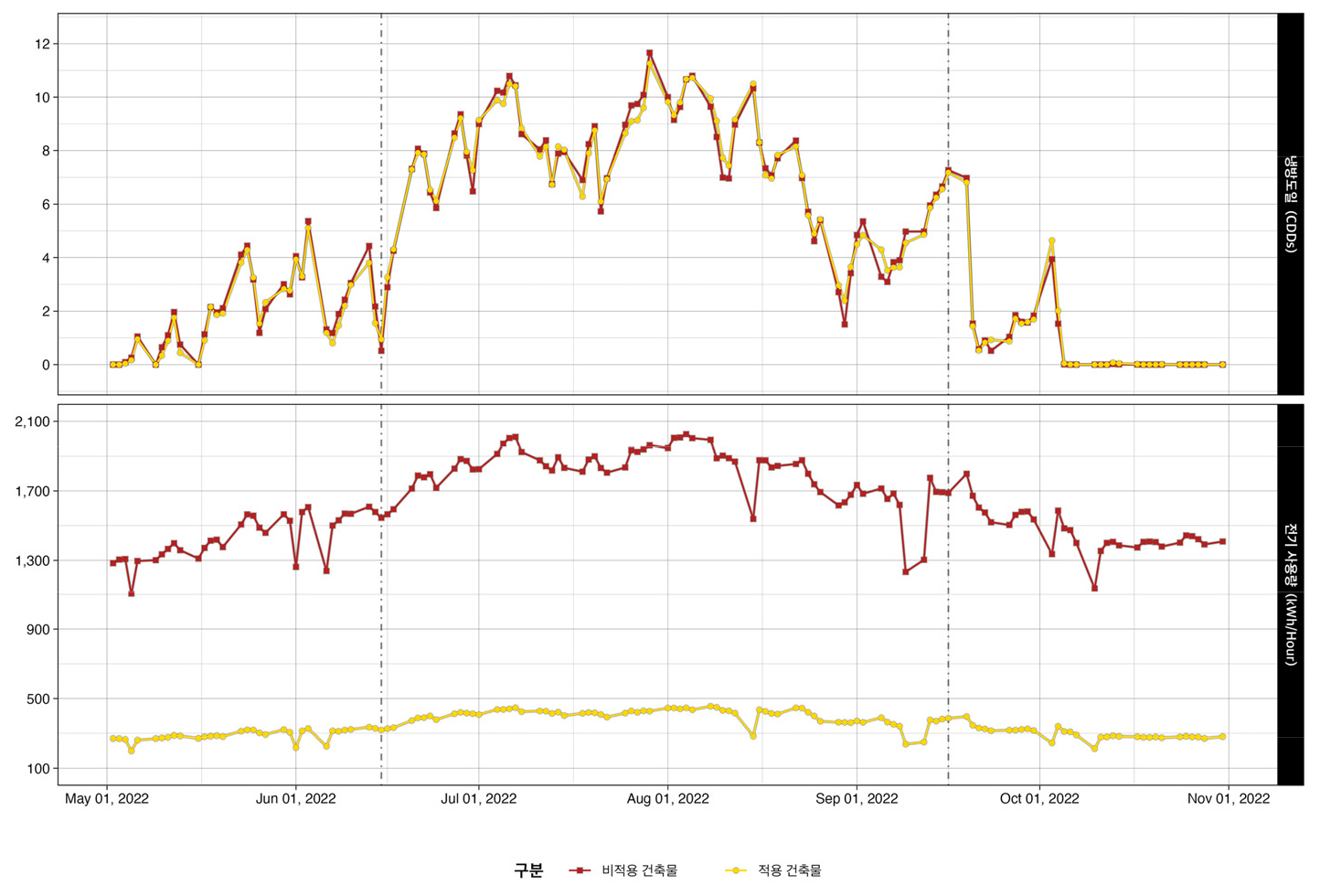
- This study evaluates the causal effect of South Korea’s Indoor Temperature Compliance Regulation―which requires public buildings to maintain indoor temperatures at or …
본 연구는 여름철 공공기관 적정실내온도 준수 규정의 전기 소비 절감 효과를 시간별 마이크로데이터에 온도 반응 함수와 이중차분법을 적용하여 인과적으로 분석하였다. 분석 결과, …
- This study evaluates the causal effect of South Korea’s Indoor Temperature Compliance Regulation―which requires public buildings to maintain indoor temperatures at or above 28°C during the summer months―on electricity consumption. Temperature Response Function (TRF) and Difference-In-Differences (DID) approaches are applied to hourly metering data for 199 public buildings over the summer of 2022. The empirical results show that while absolute electricity use in regulated buildings increased due to seasonal factors, this increase was significantly smaller than in comparable unregulated buildings―i.e., electricity consumption “increased in absolute terms but not in relative terms.” This mitigating effect is most pronounced during afternoon peak-demand hours and on particularly hot days. These findings imply that the regulation provides a cost-effective, non-price mechanism to manage peak-demand by leveraging an intuitive reference point: indoor temperature.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 여름철 공공기관 적정실내온도 준수 규정의 전기 소비 절감 효과를 시간별 마이크로데이터에 온도 반응 함수와 이중차분법을 적용하여 인과적으로 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 규제 대상 건축물의 절대적 전력 소비량은 계절적 요인으로 증가했으나, 비규제 건축물과 비교하면 증가 폭이 유의미하게 억제되었다. 즉, 규제 대상 건축물의 전력 소비가 ‘(절대적으로는) 늘었지만, (상대적으로는) 늘지 않았다.’ 이러한 효과는 전력 수요가 집중되는 오후 시간대, 그리고 집중의 정도가 높아지는 외부 온도가 높은 날에 더욱 두드러지게 나타났다. 이것은 해당 규정이 비용 효과적인 피크 수요 관리 수단이며, ‘실내 온도’와 같은 직관적인 기준점이 효과적인 비가격 메커니즘으로 작동함을 시사한다.
-
Increased but Not Increased: A Policy Impact Analysis of the Indoor Temperature Compliance Regulation
-
Research Article
-
Stimulating Distributed Energy Resources based on the Study of Foreign Distributed Energy Policy
해외 분산에너지 정책 사례 기반 국내 분산에너지 활성화 방안 연구
-
Taeyoung Jin
진태영
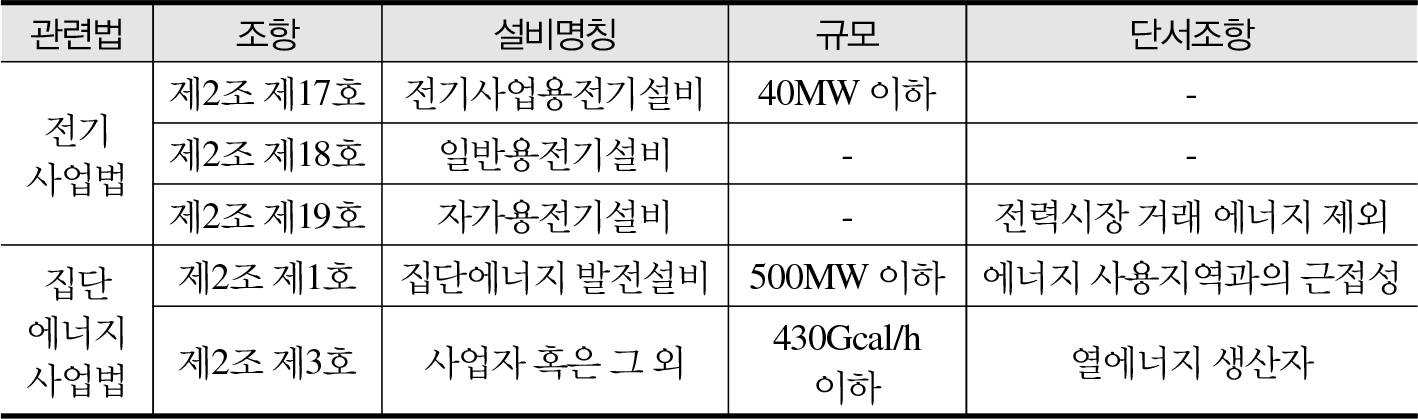
- In June 2023, the Korean government enacted the Special Act on Distributed Energy (hereinafter the “Distributed Energy Act”), which came into force …
정부는 2023년 6월 분산에너지 특별법(이하 분산법)을 제정하고, 1년 뒤인 2024년 6월에 법의 세부사항을 담은 분산에너지 특별법 시행령을 통해 분산법을 시행하였다. 중앙집중형 에너지 …
- In June 2023, the Korean government enacted the Special Act on Distributed Energy (hereinafter the “Distributed Energy Act”), which came into force in June 2024 through its presidential enforcement decree. This legislation is expected to serve as a foundational step toward transitioning from a centralized to a decentralized energy governance structure. This study examines Korea’s current legal and policy framework for distributed energy based on international policy experiences and identifies key policy instruments needed for future development. While Korea’s institutional framework—including the phased implementation strategy, legal structure, grid operations, market integration, and value-based compensation mechanisms—generally aligns with those of leading countries, it still lacks progress in critical support areas such as tariff reform, distribution system operation, utility incentive structures, and integrated resource planning. Although initiatives such as designated “Distributed Energy Zones” and grid impact assessments are underway, more proactive efforts are needed to develop complementary policy tools and viable business models. Lastly, Korea’s inclusion of thermal energy within the scope of distributed energy represents a distinct policy innovation, calling for dedicated support measures tailored to this sector.
- COLLAPSE
정부는 2023년 6월 분산에너지 특별법(이하 분산법)을 제정하고, 1년 뒤인 2024년 6월에 법의 세부사항을 담은 분산에너지 특별법 시행령을 통해 분산법을 시행하였다. 중앙집중형 에너지 거버넌스에서 지역분권형 에너지로 전환할 수 있는 초석이 될 것으로 보인다. 본 연구에서는 해외 분산에너지 정책 사례를 바탕으로 국내 분산에너지 활성화를 위해 법과 정책의 현주소를 파악하고 향후 필요한 정책도구들을 발굴한다. 우리나라 분산에너지 정책 추진체계는 단계별 접근체계, 제도프레임 및 법제화, 계통 운영 및 시장 통합, 그리고 가치평가 및 보상구조 체계 구축에 있어 해외 정책 프레임워크와 기반이 같다고 볼 수 있다. 그러나 지원정책에 있어서는 요금제 개편, 배전망 운영체계, 유틸리티 인센티브 구조 개편, 통합계획제도 운영 등에 있어서 미진한 부분이 존재한다. 분산에너지 특화지역 지정 및 전력계통영향평가 등의 세부사항이 논의되고 있지만 정책과 사업모델 발굴 병행이 지속적으로 추진되어야 할 것으로 보인다. 마지막으로, 열에너지의 분산에너지화는 우리나라의 특징적 정책이므로 별도 지원정책 발굴이 시급하다.
-
Stimulating Distributed Energy Resources based on the Study of Foreign Distributed Energy Policy
-
Research Article
-
Understanding REC Spot Price Dynamics: The Interplay of Oversupply and Market Structure
REC 현물가격 안정화를 위한 시사점: 초과공급과 현물시장 거래비중의 역할
-
Seojin Lee, Byunguk Kang
이서진, 강병욱
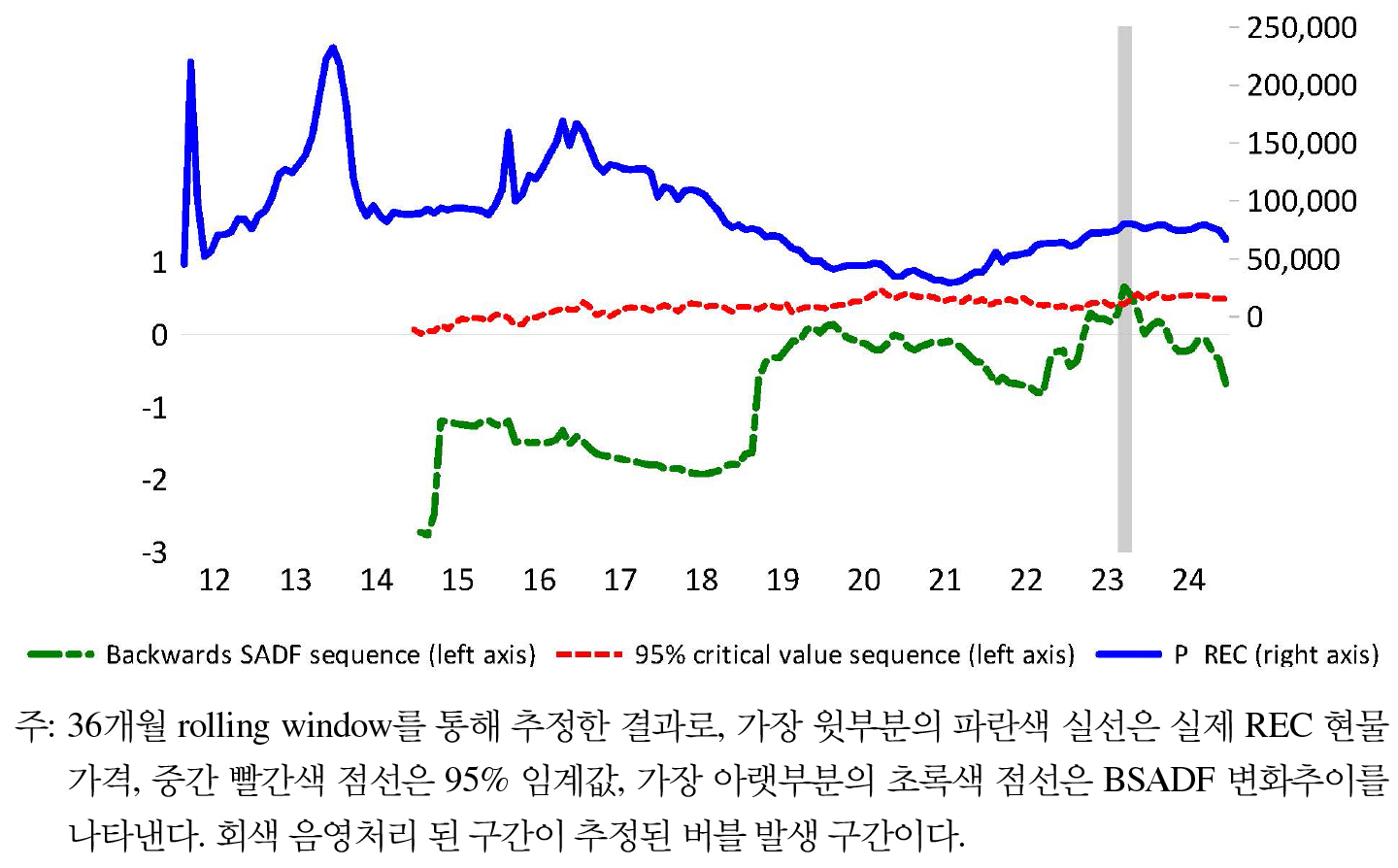
- While REC (Renewable Energy Certificate) prices have traditionally been viewed as driven by supply-demand fundamentals, the coexistence of spot and contract markets …
REC 현물가격은 전통적으로 수급 요인에 의해 결정되는 것으로 간주되어 왔으나, 현물시장과 계약시장이 병행되는 이원적 시장구조하에서는 시장 참여자의 거래 전략 변화와 거래구조의 동태적 …
- While REC (Renewable Energy Certificate) prices have traditionally been viewed as driven by supply-demand fundamentals, the coexistence of spot and contract markets allows trading strategies and structural adjustments to play a critical role in price formation. Using monthly data from January 2014 to December 2023, this study employs a Structural Vector Autoregression (SVAR) model to analyze the endogenous interplay among REC oversupply, spot market share, and spot prices. Counterfactual analysis quantifies both the direct effect of oversupply and the indirect effect via market structure. The sharp price surge in 2023 is found to result not only from reduced oversupply but also from behavioral shifts in trading patterns. These findings suggest that supply-side policies alone may be insufficient for price stabilization, highlighting the need for an integrated approach that also considers behavior of market participants.
- COLLAPSE
REC 현물가격은 전통적으로 수급 요인에 의해 결정되는 것으로 간주되어 왔으나, 현물시장과 계약시장이 병행되는 이원적 시장구조하에서는 시장 참여자의 거래 전략 변화와 거래구조의 동태적 조정이 가격 형성에 실질적인 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 본 연구는 2014년 1월부터 2023년 12월까지의 월별 자료를 활용하여, REC의 초과공급, 현물시장 내 거래비중, 현물가격 간의 내생적 상호작용을 구조적 벡터자기회귀(SVAR) 모형을 통해 실증적으로 분석하였다. 특히, 반사실적 분석(counterfactual analysis)을 통해 초과공급이 현물가격에 미치는 직접적 영향뿐만 아니라, 거래구조 변화를 매개로 한 간접효과 또한 정량적으로 추정하였다. 분석 결과, 2023년 REC 가격의 급등은 단순한 초과공급 축소만으로는 충분히 설명되기 어려우며, 시장 참여자의 거래행태 변화, 즉 현물시장으로의 거래 집중이 복합적으로 작용한 것으로 나타났다. 이는 공급 조절 중심의 기존 정책만으로는 가격 안정화에 한계가 있음을 보여주며, 향후 REC 가격의 안정적 관리를 위해서는 공급량 조절뿐 아니라, 시장 참여자의 전략적 반응을 포함한 거래행태 전반에 대한 종합적 고려가 필요함을 시사한다.
-
Understanding REC Spot Price Dynamics: The Interplay of Oversupply and Market Structure
-
Research Article

-
Time-Varying Effects of Global Oil Price Shocks on the Korean Stock Market
유형별 국제유가 충격이 한국 주식시장에 미치는 시간 가변적인 영향
-
Geon Hee Lee, Ha Yeon Kim, Young Min Kim
이건희, 김하연, 김영민
- This study investigates the time-varying effects of global oil price shocks on the Korean stock market. Following Kilian (2009), oil shocks are …
본 연구는 국제 유가충격이 한국 주식시장에 미치는 시간 가변적 영향을 분석한다. 이를 위해 Kilian(2009)을 따라 유가충격을 공급, 총수요충격, 투기적 수요충격으로 식별하고, 이들이 …
- This study investigates the time-varying effects of global oil price shocks on the Korean stock market. Following Kilian (2009), oil shocks are identified as supply shocks, aggregate demand shocks, and speculative demand shocks, and their impacts are estimated using a time-varying parameter vector autoregression model with stochastic volatility (TVP-VAR-SV). The analysis covers January 1980 to March 2024, capturing major global events. The results show that oil supply shocks generally had limited effects, though their influence intensified after COVID-19. Aggregate demand shocks exerted strong positive effects before the global financial crisis but weakened or even turned negative thereafter, indicating a structural shift. Speculative demand shocks have remained persistently influential since the 2000s, dominating the forecast error variance of stock returns. Overall, the findings highlight that the effects of oil shocks are not constant but evolve across macroeconomic conditions and market environments. These results underscore the importance of distinguishing between shock types and accounting for their time-varying nature, particularly for an open, oil-import-dependent economy like Korea.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 국제 유가충격이 한국 주식시장에 미치는 시간 가변적 영향을 분석한다. 이를 위해 Kilian(2009)을 따라 유가충격을 공급, 총수요충격, 투기적 수요충격으로 식별하고, 이들이 한국 주식시장 실질 수익률에 미치는 영향을 TVP-VAR-SV 모형을 활용하여 실증적으로 분석하였다. 분석에는 1980년 1월부터 2024년 3월까지의 데이터를 활용하였으며, 아시아 외환위기, 글로벌 금융위기, 셰일 혁명, COVID-19, 러시아-우크라이나 전쟁 등 주요 사건들을 포함하여 시기별 충격 반응의 이질성과 구조적 전환을 확인하였다. 실증 분석 결과, 공급충격은 전반적으로 미약한 영향을 보였으나 COVID-19 이후 파급력이 확대되었음을 확인하였다. 총수요 충격은 금융위기 이전에는 유의한 양(+)의 영향을 보였으나, 이후 그 영향력이 급격히 약화되거나 오히려 음(-)의 반응으로 전환되는 구조적 변화를 관측하였다. 투기적 수요충격은 2000년대 이후 강한 영향력을 보였고, 2010년대 이후에도 그 중요성이 유지되고 있다. 게다가 유형별 충격의 한국 주식시장 예측오차의 분산에 대한 기여도가 시기에 따라 유의하게 달라졌으며, 특히 투기적 수요충격이 가장 지속적이고 강한 설명력을 가짐을 확인하였다. 이러한 결과는 유가 충격의 영향이 경제 여건과 시장 환경 변화에 따라 구조적으로 달라질 수 있음을 시사한다. 이는 한국처럼 원유 수입 의존도가 높고 제조업 중심의 개방 경제에서, 유가 충격의 유형별・시기별 효과를 정량적으로 분석하는 것이 정책 수립과 시장 전망 측면에서 중요한 실질적 함의를 지닌다는 점을 강조한다.
-
Time-Varying Effects of Global Oil Price Shocks on the Korean Stock Market
-
Research Article

-
Dynamic Effects of Critical Mineral Price Shocks on Inflation in South Korea: A Comparative Analysis with Crude Oil Prices
핵심광물 가격 충격이 우리나라 물가에 미치는 동태적 영향 분석: 국제 유가와의 비교 분석
-
Dohyun Park, Jongik Kim, Jinhyoung Kim
박도현, 김종익, 김진형
- This study investigates how price shocks in critical minerals affect inflation in Korea by employing a Vector Error Correction Model (VECM). In …
본 연구는 벡터오차수정모형(VECM, Vector Error Correction Model)을 활용하여 ‘핵심광물 가격충격이 우리나라 물가에 어떤 영향을 주는지’에 대한 연구문제 규명을 시도한다. 특히 국제유가 충격과 …
- This study investigates how price shocks in critical minerals affect inflation in Korea by employing a Vector Error Correction Model (VECM). In particular, it conducts a comparative analysis between the impact of crude oil price shocks and critical mineral price shocks on Korean inflation. The analysis utilizes the Impulse Response Function (IRF) and Forecast Error Variance Decomposition (FEVD) based on the VECM framework. Furthermore, the study distinguishes between producer price index (PPI) and consumer price index (CPI) to identify the magnitude, timing, and structural differences in the transmission of price shocks. The results show that crude oil and critical minerals price shocks affect Korean inflation through distinct transmission channels and temporal structures. Crude oil price shocks exhibit strong, immediate, and short-term effects on inflation, whereas critical mineral price shocks generate gradual and cumulative long-term impacts. Although oil price shocks are more influential in the short term, critical mineral price shocks display stronger long-run effects due to their persistent nature. These findings suggest that Korea’s inflation stabilization policy should account not only for oil price volatility but also for the structural influence of critical mineral prices.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 벡터오차수정모형(VECM, Vector Error Correction Model)을 활용하여 ‘핵심광물 가격충격이 우리나라 물가에 어떤 영향을 주는지’에 대한 연구문제 규명을 시도한다. 특히 국제유가 충격과 핵심광물 가격 충격이 우리나라 물가에 미치는 영향의 차이를 비교분석한다. 연구문제 규명을 위해 VECM 기반 충격반응함수(IRF, Impulse Response Function)와 예측오차분산분해(FEVD, Forcast Error Variance Decomposition)방법을 활용하여 분석하였다. 또한, 물가를 생산자물가(PPI)와 소비자물가(CPI)로 구분하여 국제유가와 핵심광물 가격의 영향력 정도, 영향 시차 및 구조적 차이를 식별하였다. 분석 결과, 국제유가와 핵심광물 가격 충격은 국내 물가에 서로 상이한 경로와 시간적 구조로 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 유가 충격은 물가에 단기적이고 즉각적인 파급효과가 강하게 나타나는 반면, 핵심광물 가격 충격은 물가에 점진적이고 누적적인 장기 파급 효과가 두드러졌다. 반응 강도는 단기적으로는 유가 충격이 강하게 나타났으나, 장기적으로는 누적적 효과로 인해 핵심광물 가격 충격이 더 강하게 나타났다. 이는 한국의 물가안정 정책에 있어 유가와 함께 핵심광물 가격의 구조적 영향 또한 반드시 고려해야 함을 시사한다.
-
Dynamic Effects of Critical Mineral Price Shocks on Inflation in South Korea: A Comparative Analysis with Crude Oil Prices
-
Research Article
-
Impact of Climate Change on Residential Electricity Consumption in Gwangju Metropolitan City by 2050
기후변화가 2050년에 광주광역시의 주거용 전력 소비에 미치는 영향
-
Dmitriy Li, Juhee Jeong, Jeong Hwan Bae
이드미트리, 정주희, 배정환
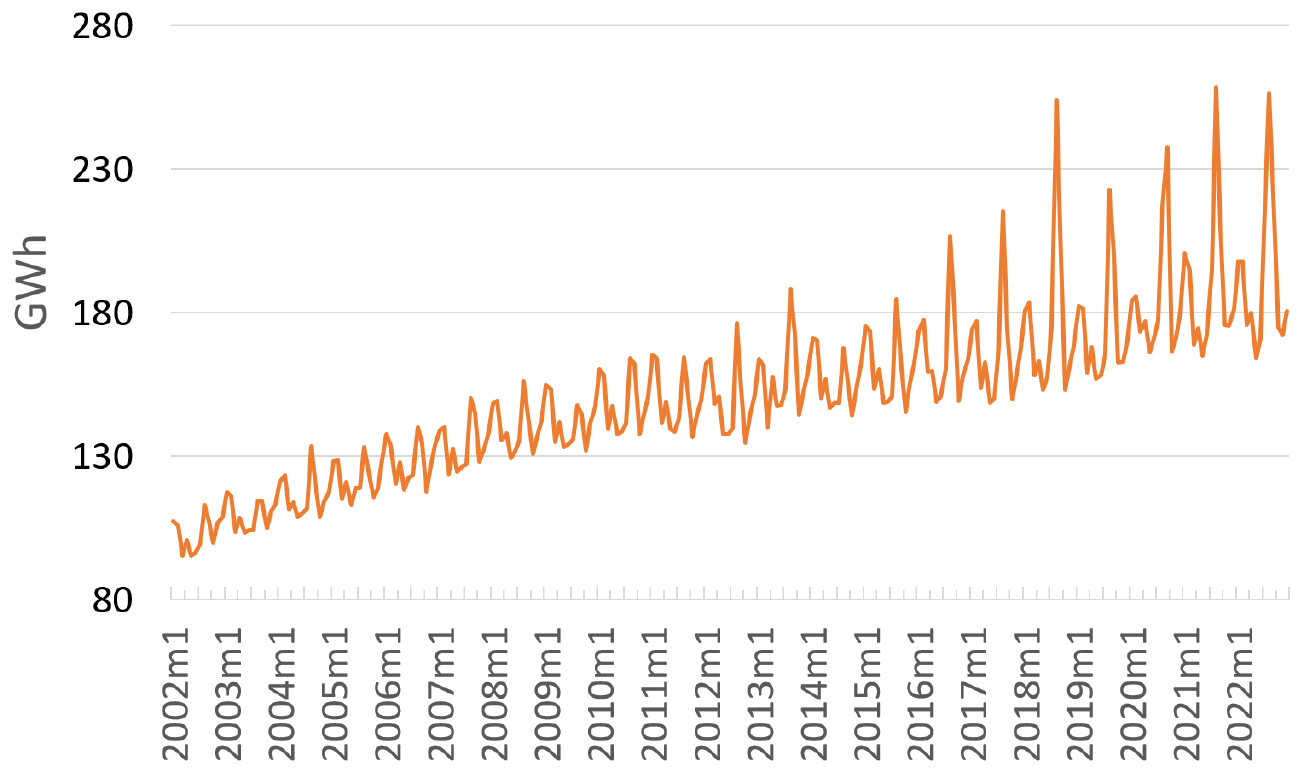
- This study examines the impact of climate change on residential electricity consumption, CO2 emissions, and associated carbon costs in Gwangju Metropolitan …
본 연구는 공유사회경제경로(SSP3-7.0) 시나리오 하에서 광주광역시의 기후변화가 가정용 전력소비, CO2 배출량, 그리고 탄소 비용에 미치는 영향을 분석하였다. 분석에는 자기회귀시차분포(ARDL) 모형을 활용하였으며, …
- This study examines the impact of climate change on residential electricity consumption, CO2 emissions, and associated carbon costs in Gwangju Metropolitan City, South Korea, under Shared Socioeconomic Pathway (SSP3-7.0) scenario. Using an Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) model, we analyze the long-term relationship between electricity consumption and key variables, including average temperature, its squared term, precipitation, the share of single-person households, cooling and heating degree days. The estimation results confirm a statistically significant U-shaped relationship between temperature and electricity consumption, with demographic shifts also emerging as major contributors to rising demand. In contrast, precipitation and degree days show no significant effects. Applying the model’s elasticities to SSP3-7.0 projections, we estimate that annual residential electricity consumption will increase by 4.8% in 2040 and 9.5% in 2050 relative to 2022, with the largest increases occurring in summer. Under the NGFS “Fragmented World” scenario, the annual carbon cost is projected to rise from 46 million KRW in 2023 to nearly 48.7 billion KRW by 2050. These findings highlight the urgent need for demand-side management and integrated climate-energy strategies to address the growing environmental and economic burdens of climate change in the residential energy sector.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 공유사회경제경로(SSP3-7.0) 시나리오 하에서 광주광역시의 기후변화가 가정용 전력소비, CO2 배출량, 그리고 탄소 비용에 미치는 영향을 분석하였다. 분석에는 자기회귀시차분포(ARDL) 모형을 활용하였으며, 평균기온, 기온의 제곱항, 강수량, 1인 가구 비율, 냉난방도일 등을 주요 변수로 설정하였다. 분석 결과, 기온과 전력 소비 간에는 통계적으로 유의한 U자형 관계가 확인되었으며, 인구 구조 변화 또한 전력 수요 증가의 주요 요인으로 나타났다. 반면, 강수량과 냉・난방도일은 유의미한 영향을 보이지 않았다. SSP3-7.0 시나리오에 따르면, 2040년과 2050년의 연간 가정용 전력소비는 2022년 대비 각각 4.8%, 9.5% 증가할 것으로 전망된다. 특히, 여름철 증가 폭이 두드러질 것으로 나타났다. NGFS의 ‘분절적 세계(Fragmented World)’ 시나리오에 따른 외생적 탄소가격 경로를 적용한 결과, 연간 탄소 비용은 2023년 4,600만 원에서 2050년 약 487억 원으로 증가할 것으로 추정되었다. 본 연구는 기후변화가 가정용 에너지 부문에 가져올 환경적・경제적 부담을 완화하기 위해 수요관리 강화 및 통합적인 기후-에너지 전략이 시급하다는 점을 시사한다.
-
Impact of Climate Change on Residential Electricity Consumption in Gwangju Metropolitan City by 2050
-
Research Article
-
Ultra-High Voltage Transmission and Corporate Operational Risk: Evidence from China
초고압 송전망과 기업의 운영 리스크: 초고압 전력망의 경제적 효과
-
Han Sun, Jae Ho Lee, Hyoung Goo Kang, Guodong Zhang
손한, 이재호, 강형구, 장국동
- This study investigates the causal impact of China’s Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) transmission infrastructure on corporate operational risk. As a cornerstone of the …
본 연구는 중국의 초고압(UHV) 송전 인프라가 기업의 운영 리스크에 미치는 인과적 영향을 실증적으로 분석한다. UHV 전력망은 자원이 풍부한 서부 지역의 전력을 산업화된 …
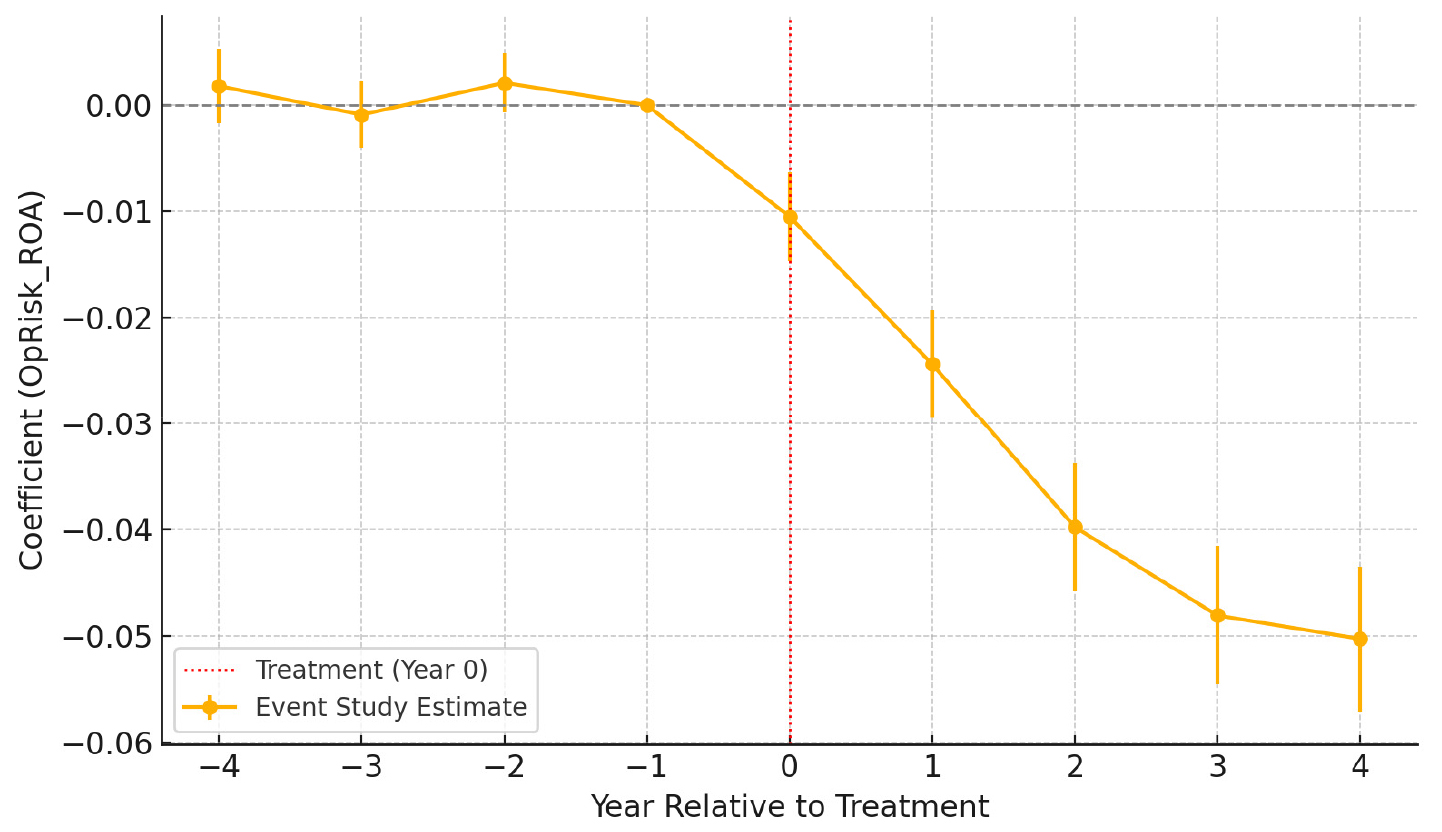
- This study investigates the causal impact of China’s Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) transmission infrastructure on corporate operational risk. As a cornerstone of the national energy strategy, the UHV grid enables the efficient transfer of electricity from resource-rich western regions to industrialized eastern provinces, fundamentally reshaping the energy landscape for firms. Leveraging the staggered rollout of UHV projects from 2007 to 2016 as a quasi-natural experiment, we employ a robust Difference-in-Differences framework using the Callaway and Sant’Anna (2020) estimator to identify the dynamic treatment effects. The analysis reveals that UHV commissioning significantly reduces firms’ operational risk, measured by the volatility of Return on Assets (ROA), with the effect growing in magnitude over time. Mechanism analyses suggest that this reduction is partially mediated by increased green innovation and enhanced financial flexibility. The heterogeneity analysis indicates that the effect is stronger for non-state-owned enterprises, firms in energy-intensive industries, and those located in power-receiving provinces. These findings highlight the firm-level benefits of large-scale public infrastructure and offer valuable implications for policymakers, managers, and investors regarding the strategic importance of energy stability. The study contributes to the literature by connecting macro-level infrastructure policy with micro-level corporate risk and innovation outcomes.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 중국의 초고압(UHV) 송전 인프라가 기업의 운영 리스크에 미치는 인과적 영향을 실증적으로 분석한다. UHV 전력망은 자원이 풍부한 서부 지역의 전력을 산업화된 동부 연안으로 효율적으로 전달함으로써, 기업의 에너지 환경을 근본적으로 변화시키는 국가 전략 핵심 사업이다. 본 연구는 2007년부터 2016년까지의 시차를 두고 단계적으로 구축된 UHV 프로젝트를 준자연실험(quasi-natural experiment)으로 활용하며, Callaway and Sant’Anna(2020)의 추정 방법을 적용한 차분의 차분(DID) 분석을 통해 인과 효과를 식별한다. 분석 결과, UHV 라인의 준공은 기업의 자산수익률(ROA) 변동성으로 측정한 운영 리스크를 통계적 및 경제적으로 유의하게 감소시키며, 이 효과는 시간이 지남에 따라 점진적으로 확대되는 것으로 나타났다. 메커니즘 분석을 통해 이러한 리스크 감소는 기업의 녹색 혁신 활동 증가 및 재무적 유연성 제고에 의해 부분적으로 매개됨을 확인하였다. 이 효과는 비국유기업, 에너지 집약 산업군, 그리고 전력 수입 지역에 위치한 기업에서 특히 강하게 나타난다. 본 연구는 대규모 공공 인프라 투자에 따른 긍정적 외부효과를 기업 수준에서 정량적으로 규명하며, 에너지 인프라 안정성이 기업 리스크와 혁신 활동에 미치는 구조적 영향을 조명함으로써 정책결정자, 기업 경영진, 투자자에게 유의미한 시사점을 제공한다.
-
Ultra-High Voltage Transmission and Corporate Operational Risk: Evidence from China
-
Research Article
-
An Empirical Analysis on the Duality of the Direct Power Purchase Scheme: Focusing on Participant Benefits, Market Risk, and Cost Shift
전력직접구매제도의 양면성에 대한 실증 분석: 참여자 편익, 시장 리스크, 비용 전가를 중심으로
-
Yeonchan Jeong
정연찬
- This study analyzes three key aspects of Korea’s recently activated Direct Power Purchase (DPP) scheme: participant benefits, market risks, and cost-shifting effects. …
본 연구는 최근 활성화되고 있는 전력직접구매제도가 갖는 참여자 편익, 시장 리스크, 비용 전가라는 세 가지 핵심적인 측면을 계량적으로 분석하고 정책적 시사점을 도출하고자 …
- This study analyzes three key aspects of Korea’s recently activated Direct Power Purchase (DPP) scheme: participant benefits, market risks, and cost-shifting effects. The analysis employs three quantitative methods based on defined assumptions and scenarios: a cost-benefit analysis, a System Marginal Price (SMP) sensitivity analysis, and a participation rate scenario analysis. The results confirm that the DPP scheme provides clear financial benefits to participants in the current SMP environment. However, it also exposes them to significant market price risk, with a calculated break-even point of approximately 141.5 KRW/kWh, above which participants would incur financial losses. Furthermore, a simulation based on the assumption that the incumbent utility’s revenue losses are transferred to its remaining customers reveals a “cost-shift” phenomenon. This effect shows that the pressure for tariff increases accelerates non-linearly as the DPP participation rate grows. These findings offer quantitative evidence for the potential impacts of the scheme and highlight that the principles of cost allocation and their implementation will be critical policy variables in future discussions.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 최근 활성화되고 있는 전력직접구매제도가 갖는 참여자 편익, 시장 리스크, 비용 전가라는 세 가지 핵심적인 측면을 계량적으로 분석하고 정책적 시사점을 도출하고자 하였다. 이를 위해 비용 분석, SMP 민감도 분석, 참여율 시나리오 분석 등 시나리오에 기반한 세 가지 계량 분석을 수행하였다. 분석 결과, 전력직접구매제도는 현재 수준 SMP 환경에서 참여자에게 명확한 재무적 편익을 제공하지만, SMP가 약 141.5원/kWh의 손익분기점을 넘어서면 오히려 손실이 발생하는 높은 시장 가격 리스크를 내포하고 있음을 확인하였다. 또한, 한전의 수익 감소분이 오직 잔존 산업용 소비자에게 전가된다는 가정하에 수행된 시뮬레이션에서는, 제도 참여율이 높아질수록 잔존 소비자의 요금 인상 압박이 비선형적으로 가속화되는 ‘비용 전가(Cost Shift)’ 현상이 나타났다. 이상의 분석 결과는 제도의 잠재적 파급효과에 대한 정량적 근거를 제시하며, 향후 제도 논의에 있어 모든 참여자 간의 비용 분담 원칙과 그 구현 방식이 핵심적인 정책 변수가 될 것임을 시사한다.
-
An Empirical Analysis on the Duality of the Direct Power Purchase Scheme: Focusing on Participant Benefits, Market Risk, and Cost Shift


 Korean Energy Economic Review
Korean Energy Economic Review



